SALES – B2B Crystal sugar
General
Sugar, the general term used for the carbohydrate sucrose, is found in many plants and especially in sugar beets and sugar cane. Crystal sugar is obtained from the cell sap of sugar beets in a process of gentle extraction, purification and crystallization in the following purity classes: white sugar EC category I (“refined sugar”) and white sugar EC category II (“white sugar”).
Products and applications
The industrial use of sugar for producing confectionery goods, bakery goods, chocolate, nutrients, delicatessen, fruit preparations, beverages, dairy products and other products can essentially be traced back to three basic processes, milling, mixing and dissolving. In all three cases, the process and possibly the quality of the products are influenced by the size distribution of the sugar crystals used.
Coarse sugars in particular are advantageous for milling processes. The larger crystal mass promotes the initial crushing and ensures uniform grain size ranges in the final product. For mixtures, fine sugar fractions are preferred as their smaller crystal mass and larger specific surface improves the mixing quality of the end-products (beverages from vending machines, cake mixes, instant products, etc.)
The use of a uniform fraction with medium-sized crystals is recommended to ensure that the crystal sugar dissolves rapidly and completely when producing concentrated sugar solutions for beverages, caramels, fruit preparations, etc. A particularly highly concentrated sugar solution is frequently boiled in a first stage when producing confectionery goods (sweets, fruit gums, licorice). The rate at which the sugar dissolves is critical for ensuring a rapid, gentle overall process. Due to the small specific surface area, coarse sugar dissolves fairly slowly, while fine sugars tend to cause more laminar flow conditions in stirred tanks with high sugar concentration, which in turn reduces the rate of dissolution.
Specially sieved crystal size ranges are available for milling, mixing and dissolving:
| White sugar EC category II (“white sugar”) | White sugar EC category I (“refined sugar”) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applications | w0 | w2 | w3 | w4 | w5 | w6 | w8 | w9 | w10 | w11 | w12 | r2 | r3 | r4 | r5 | r6 | r7 | r8 | r9 | r10 | r11 |
| Milling | w0 | w2 | w3 | w4 | r2 | r3 | r4 | ||||||||||||||
| Mixing | w5 | w6 | w8 | w9 | w10 | w11 | w12 | r5 | r6 | r7 | r8 | r9 | r10 | r11 | |||||||
| Dissolving | w0 | w4 | w5 | w6 | r4 | r5 | r6 | ||||||||||||||
The following overview is intended as a guide, with recommendations for different applications:
| White sugar EC category II (“white sugar”) | White sugar EC category I (“refined sugar”) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applications | w0 | w2 | w3 | w4 | w5 | w6 | w8 | w9 | w10 | w11 | w12 | r2 | r3 | r4 | r5 | r6 | r7 | r8 | r9 | r10 | r11 |
| Confectionery | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Chocolate | w0 | w3 | w4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Caramel candies | w0 | w3 | w4 | r4 | |||||||||||||||||
| Jelly beans | w0 | w4 | w6 | r4 | |||||||||||||||||
| Sugar-coated products | w5 | w6 | w8 | w9 | r9 | r10 | |||||||||||||||
| Popcorn | w2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Liquid-filled chocolate candies | r3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Beverages | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Spirits | w0 | w4 | r4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Soft drinks | w0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Bakery | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Bakery products/ mixtures | w4 | w5 | w6 | w10 | w11 | w12 | r2 | r3 | r4 | r5 | r6 | r7 | r8 | r10 | r11 | ||||||
| Decorating crystal sugars | w4 | w8 | r2 | r8 | |||||||||||||||||
| Processed foods | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Spreads | w0 | w3 | w4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Instant products | w6 | w8 | w9 | w10 | r4 | ||||||||||||||||
| Vanillin sugar | r5 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Delicatessen products | w0 | w4 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Dairy products | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Ice cream | w0 | w5 | w6 | r7 | r10 | r11 | |||||||||||||||
| Milk products | w0 | w4 | w10 | w11 | w12 | r4 | |||||||||||||||
| Other | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Pharmaceutical products | r4 | r8 | r9 | r11 | |||||||||||||||||
| Fruit preparation1 | w0 | w3 | w4 | r3 | r4 | ||||||||||||||||
Summary of range
White sugar EC category I (refined sugar) is made from white sugar EC category II with an additional crystallization step and is characterized by particularly high purity.Pfeifer & Langen supplies both types of crystal sugars in different crystal sizes for different applications. Organic crystal sugars which comply with the Council Regulation (EC) are available for the production of organic products.
Analytical data
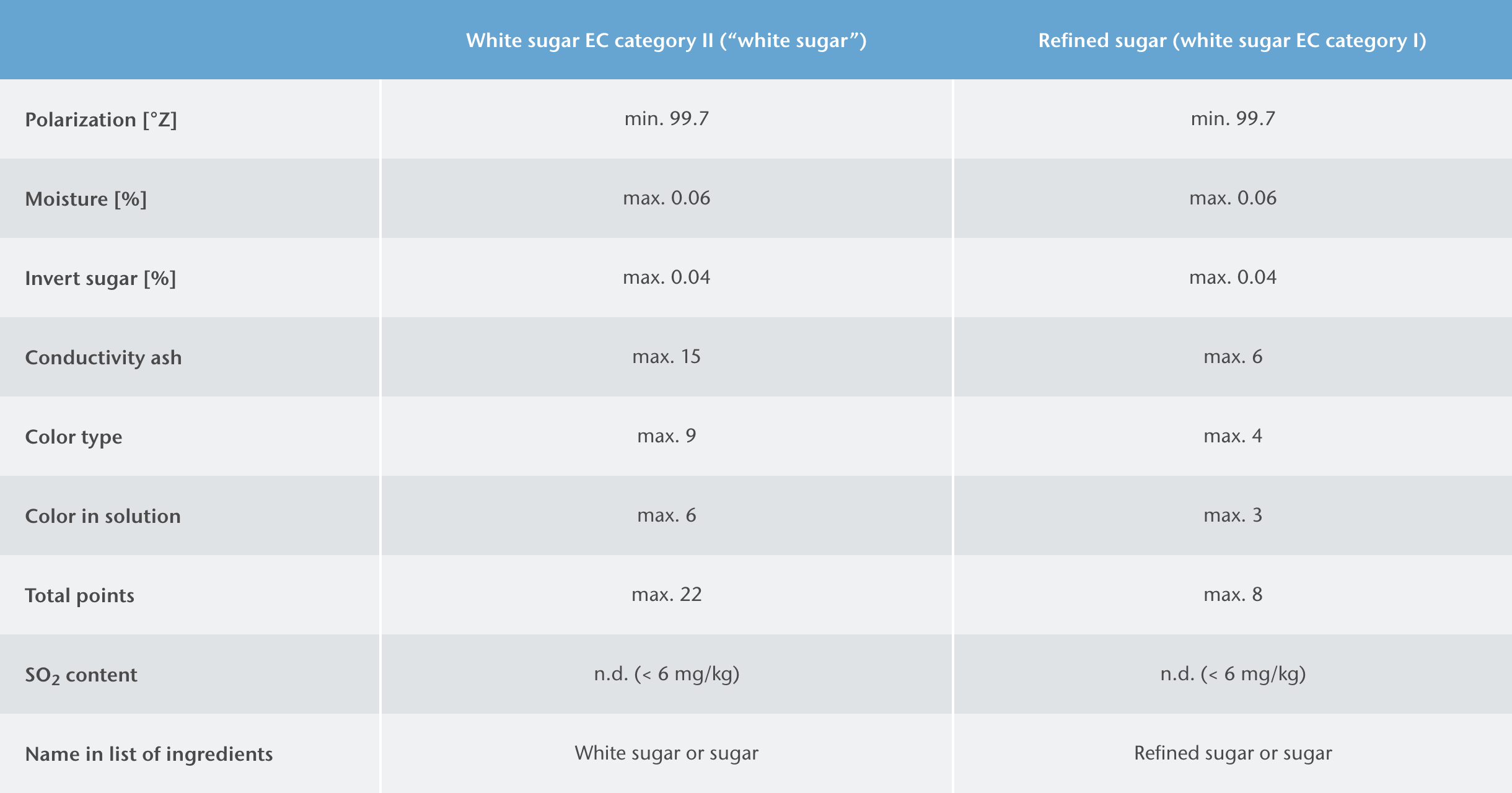
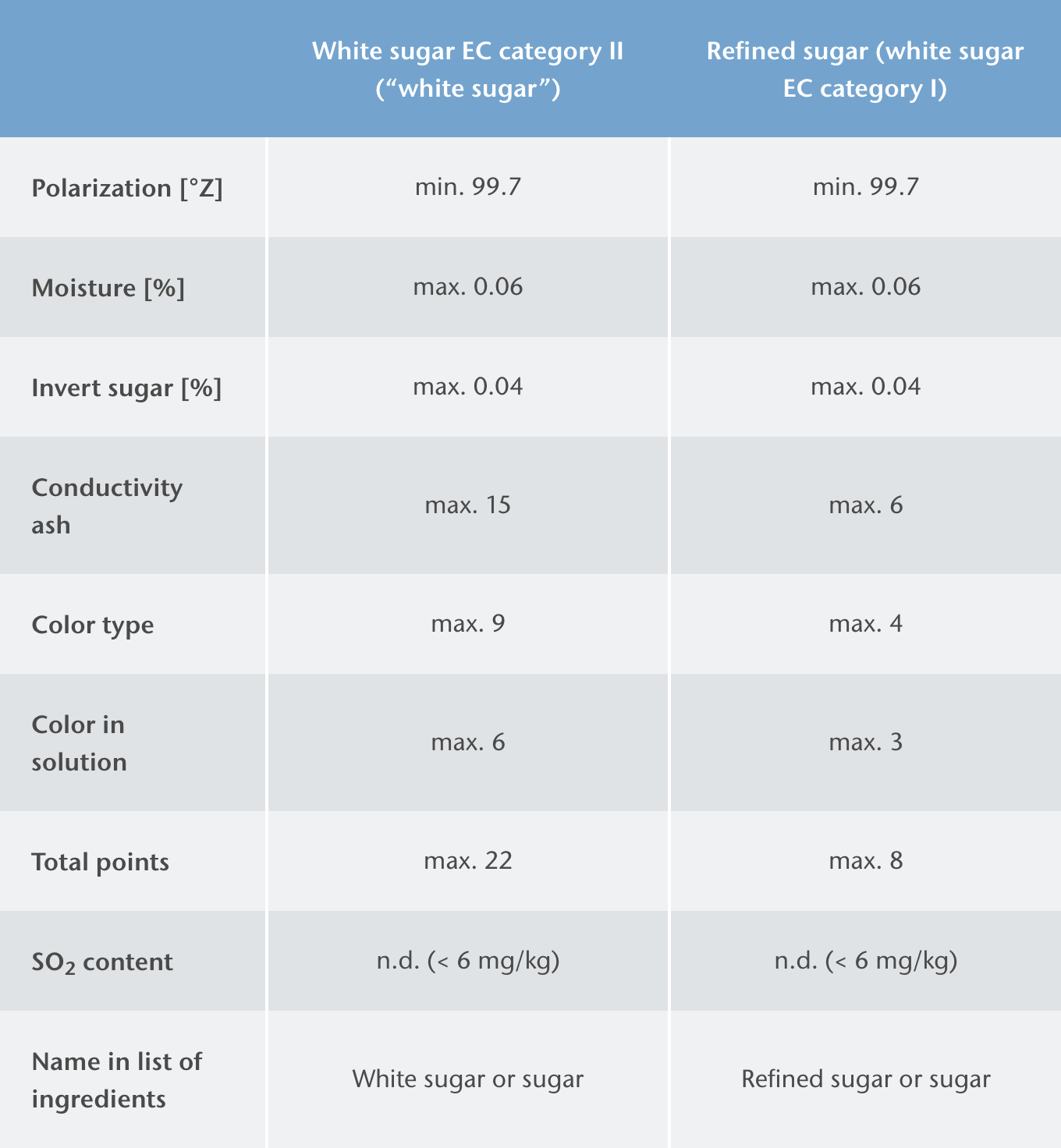

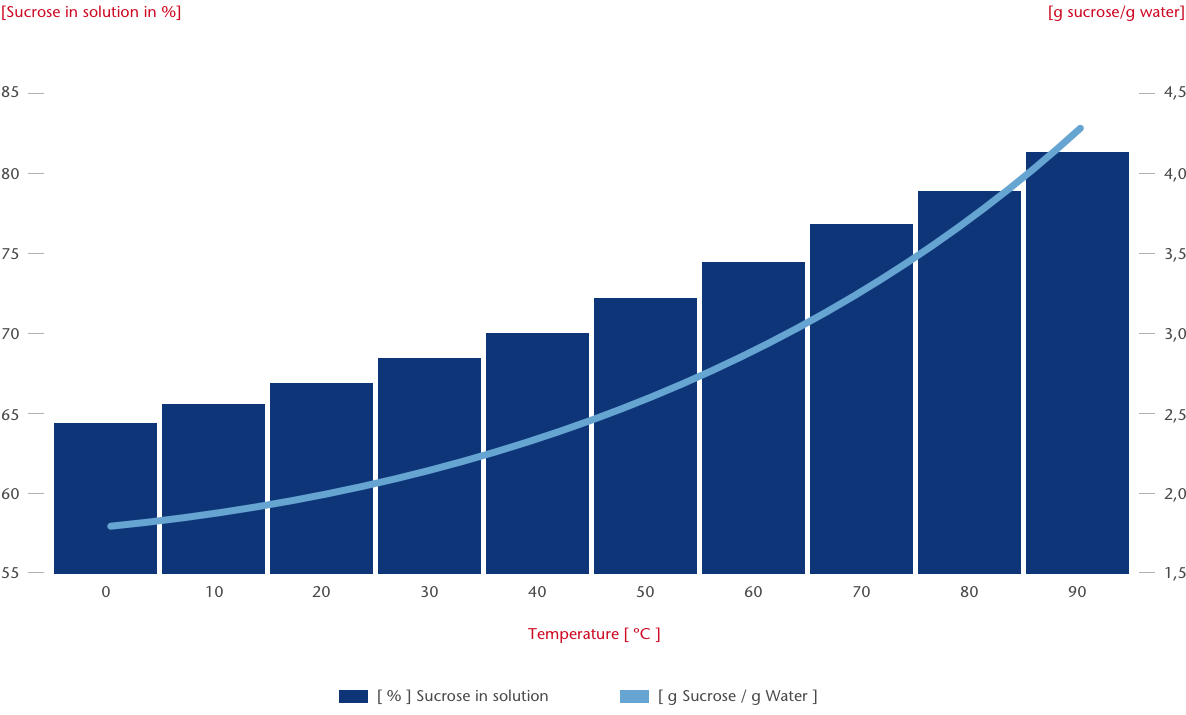
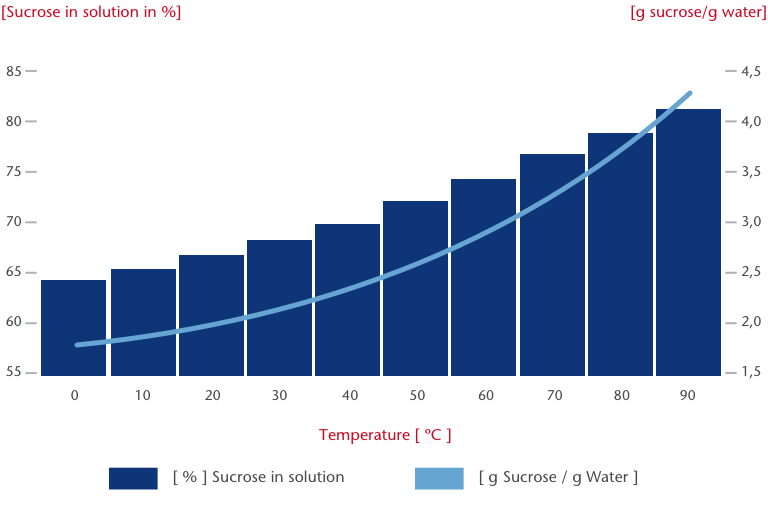
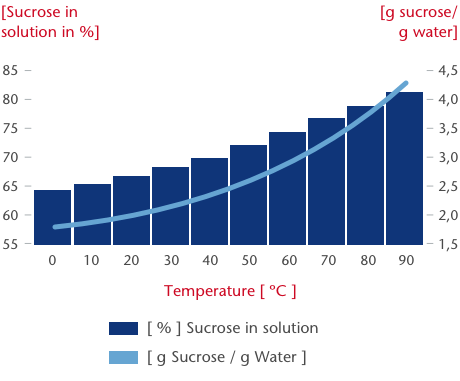
Solubility of sucrose
Forms supplied
- Bulk
- Big Bag
- Bags in different formats